SMC trading, or Smart Money Concepts, is an advanced forex strategy that helps traders align with institutional market movements. Instead of relying on traditional retail indicators, SMC trading focuses on liquidity, market structure, order flow, and manipulation. By understanding how banks, hedge funds, and institutions influence price action, traders can gain a strategic advantage in the forex market.
What is SMC Trading?
SMC trading is a methodology that examines price action based on institutional market behavior. It moves beyond simple support and resistance, focusing on how and why price moves. The core idea is that smart money—large financial institutions—control price movements, and retail traders who recognize their footprints can make better trading decisions.
Why Smart Money Concepts Matter
Unlike conventional strategies that rely on indicators, SMC trading is rooted in real-time price movements. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Market Insight – Traders understand the real driving forces behind price action.
- Better Entry and Exit Points – By recognizing liquidity zones and institutional orders, traders can optimize their entries.
- Stronger Risk Management – Identifying manipulations helps avoid stop hunts and fake breakouts.
Key Elements of Smart Money Concepts
SMC trading is built on several core principles that traders use to analyze market behavior effectively:
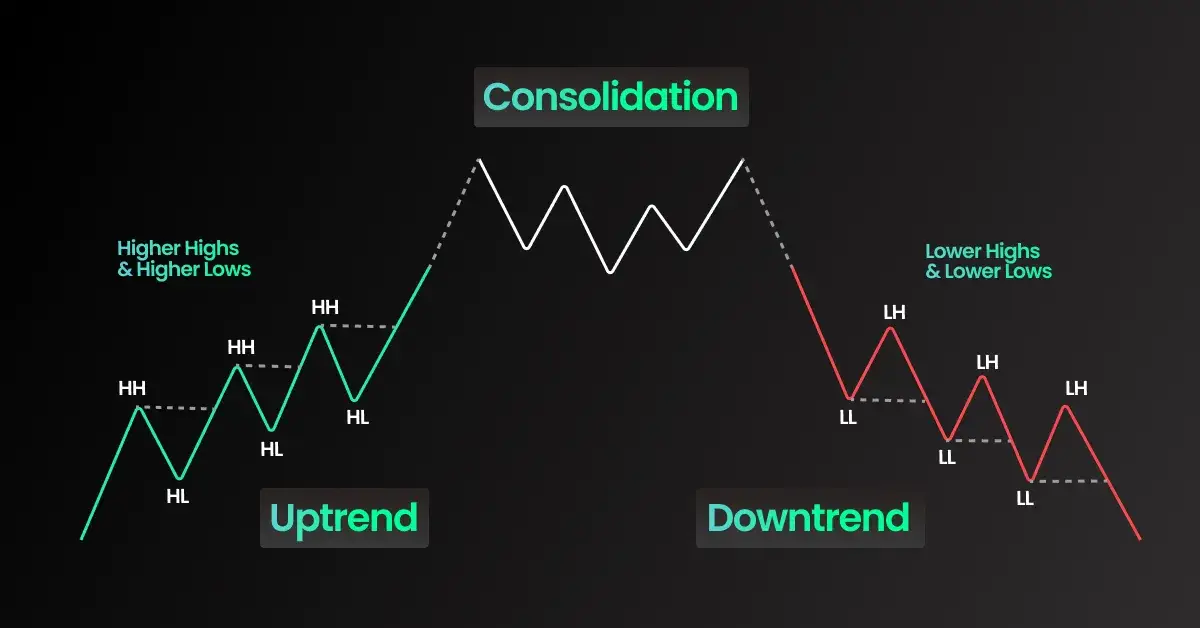
Market Structure
Market structure refers to the trend of price movements over time. Traders classify price action into three main phases:
| Market Condition | Characteristics | Trading Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Uptrend | Higher highs and higher lows | Look for buying opportunities |
| Downtrend | Lower highs and lower lows | Look for selling opportunities |
| Consolidation | Sideways price movement | Wait for breakout confirmation |
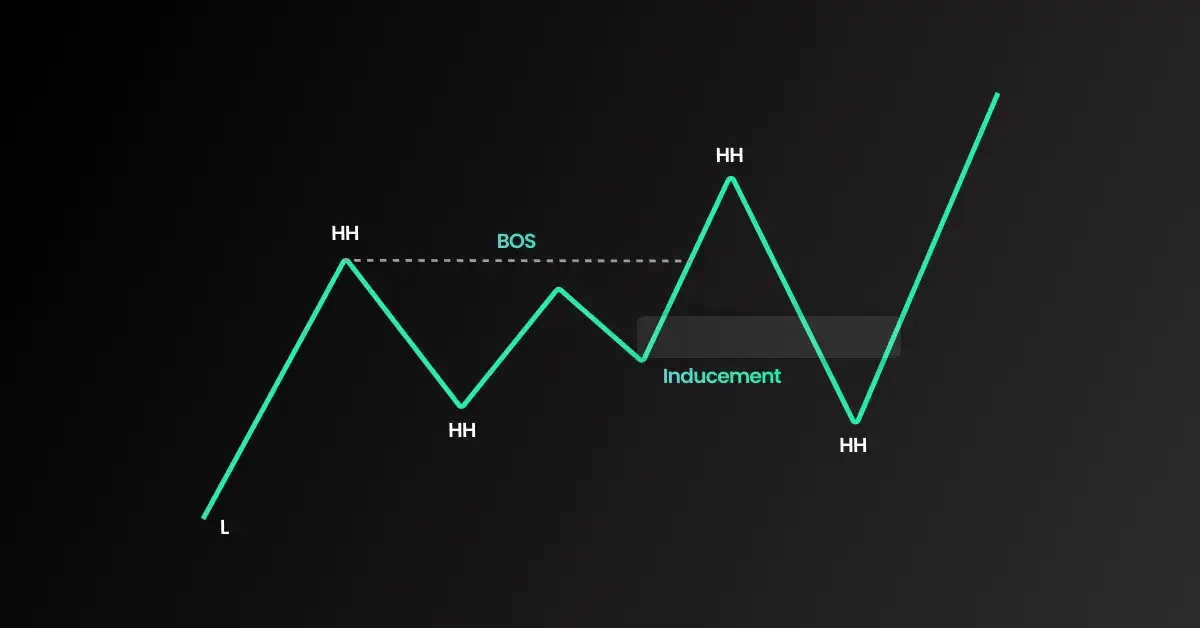
A break of structure (BOS) occurs when price surpasses a key high or low, indicating a potential trend shift. Recognizing this helps traders make informed trading decisions.
Liquidity and Stop Hunts
Institutions seek liquidity to execute large orders without causing excessive price slippage. They create liquidity pools near:
- Swing highs and swing lows – Price often spikes past these levels before reversing.
- Round numbers – Common areas where retail traders place stop-loss orders.
- Key support and resistance zones – Institutional traders manipulate these levels before executing trades.
Understanding liquidity helps traders avoid common retail traps and position themselves in line with institutional moves.
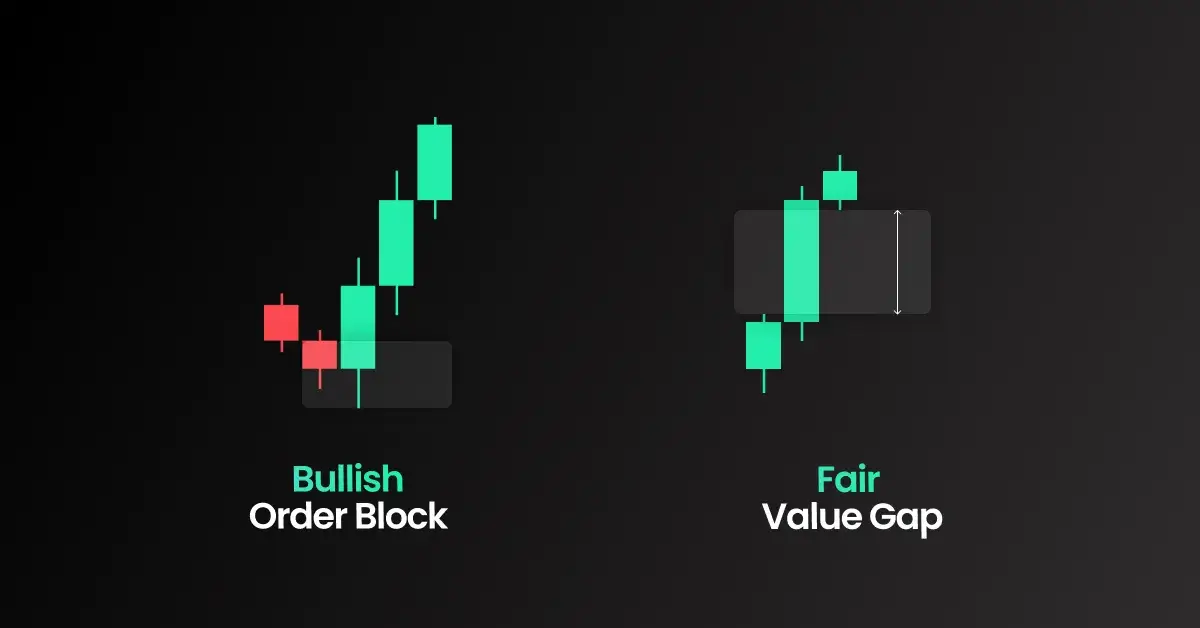
Order Blocks
Order blocks are consolidation zones where institutions place large buy or sell orders before a major price move. They act as strong support or resistance levels.
Traders use order blocks as high-probability entry points, waiting for price to return to these areas before executing a trade. A valid order block typically:
- Forms before a significant price movement.
- Appears with a strong bullish or bearish candle.
- Shows a clear reaction when price revisits the level.
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs)
A Fair Value Gap occurs when price moves rapidly in one direction, leaving an imbalance in liquidity. These gaps are often filled later as price retraces before continuing the trend.
FVGs help traders:
- Identify potential retracement zones for re-entry.
- Confirm trend direction after an imbalance is corrected.
- Improve trade timing by waiting for fair value areas.
Inducement and Market Manipulation
Retail traders often fall into inducement traps, where price movements appear to break out but later reverse. Smart money creates these traps to trigger stop-loss orders before continuing in the intended direction.
Common manipulation patterns include:
- False breakouts – Price temporarily moves beyond a key level before reversing.
- Liquidity grabs – Institutions push price toward stop-loss areas before entering their own positions.
- Engineered liquidity zones – Price consolidates in a tight range before a large institutional move.
Applying SMC Trading in Forex
Traders use Smart Money Concepts by integrating key techniques into their trading strategies.
How to Identify Market Structure Shifts
- Determine the trend – Identify whether the market is forming higher highs (uptrend) or lower lows (downtrend).
- Look for break of structure (BOS) – A strong candle breaking a key level signals a potential shift.
- Confirm with liquidity zones – Ensure there is a reason for the breakout (liquidity grab, institutional order flow).
Using Order Blocks for Entries
- Identify strong order blocks where price previously reversed sharply.
- Wait for price to revisit the order block before placing a trade.
- Use additional confirmations, such as FVGs or liquidity sweeps, to validate the entry.
Avoiding Retail Traps and False Signals
To stay ahead of institutional manipulation, traders should:
- Avoid trading breakouts immediately – Wait for confirmation that the breakout is genuine.
- Recognize stop hunts – Institutions often push price beyond key levels before reversing.
- Combine multiple SMC concepts – Use liquidity, order blocks, and fair value gaps together for better trade setups.
Risk Management in SMC Trading
- Set stop-loss orders – Place stops beyond liquidity zones to avoid stop hunts.
- Use a risk-reward ratio – Aim for at least 1:2 or 1:3 risk-reward ratios.
Adjust lot sizes accordingly – Ensure risk remains consistent across trades.
Final Thoughts: Is SMC Trading Right for You?
SMC trading is ideal for traders looking to follow institutional order flow instead of relying on retail indicators. It offers a data-driven approach to understanding market movements but requires patience and in-depth analysis.
Who Should Use SMC Trading?
- Traders who prefer price action over lagging indicators.
- Those looking to align their strategies with institutional traders.
- Individuals willing to study market structure and liquidity.
By mastering Smart Money Concepts, traders can avoid common retail mistakes and increase their chances of success in the forex market.
Q&A for SMC Trading
1. What is SMC in trading?
SMC (Smart Money Concepts) in trading is a strategy that focuses on institutional market movements rather than traditional retail trading indicators. It helps traders understand liquidity, order flow, market structure, and price manipulation by large financial institutions such as banks and hedge funds. By following smart money behavior, traders can align their trades with the market’s dominant forces.
2. Does SMC trading really work?
Yes, SMC trading can be highly effective for traders who master its principles. Since it is based on institutional order flow and liquidity zones, it provides deeper insights into market movements compared to conventional retail strategies. However, success in SMC trading requires patience, discipline, and a thorough understanding of price action, market structure, and liquidity dynamics.
3. What is the meaning of SMC?
SMC stands for Smart Money Concepts, a trading methodology that focuses on understanding how large financial institutions influence price action. It aims to identify liquidity traps, order blocks, fair value gaps (FVGs), and market manipulations to help traders enter and exit trades more effectively. Instead of relying on lagging indicators, SMC trading emphasizes real-time market behavior.
Summary of SMC Trading Concepts
| Concept | Definition | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Break of Structure (BOS) | Key level break | Confirms trend continuation |
| Change of Character (CHoCH) | Market direction reversal | Signals potential reversals |
| Liquidity Zones | Areas where institutions hunt stops | Helps avoid false breakouts |
| Order Blocks | Institutional buy/sell zones | Provides strong support/resistance |
| Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) | Market imbalances | Acts as price rebalancing areas |